Khashayar Shojaei-asanjan
Process of Engineering Design from Personal Experience
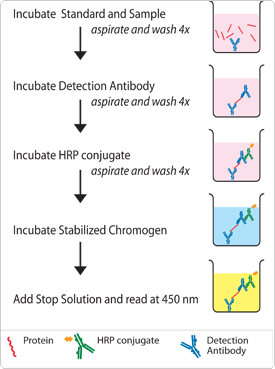
ELISA(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a diagnostic test for detecting and measuring the concentration of a specific antibody or antigen present in a solution. ELISA is performed in following steps:
1- Interior walls of the plate are coated with the antigen of interest
2- Wells are then filled with dilutions of patient's serum
3- The antibodies in the serum specific to the antigen will bind to the antigen
4- The well are washed out to remove the unbound antibodies
5-Then the solution of animal antibody against human antibody is added, these antibodies are covalently conjugated to an enzyme
6-The solution is removed once again to remove the unbound enzyme-conjugated antibodies
7-Finally, the solution containing the substrate is added, the reaction of the substrate with the animal antibody produces a detectable colour in the solution
The high incidence of disease coupled with the lack of capacity to perform sufficient diagnosis in laboratories pose serious problem in third-world countries. The barries are highly due to the lack of technical training and required resources. To compensate for this shortage, the automation of ELISA is a necessity. Hence, our team was given the task of producing and presenting the robotic dispenser capable of autonomously performing the ELISA.
Biomedical Engineering Competition(BMEC) 2014: Automating ELISA(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
Attachments
 Robotic Dispenser |  BMEC Team |  Competing Designs |
|---|---|---|
 Presentation Room |  Final Design |  Testing the Design |
 Testing the Design |  First Design(alternative design) |  Working on Final Design |
 Work Station |